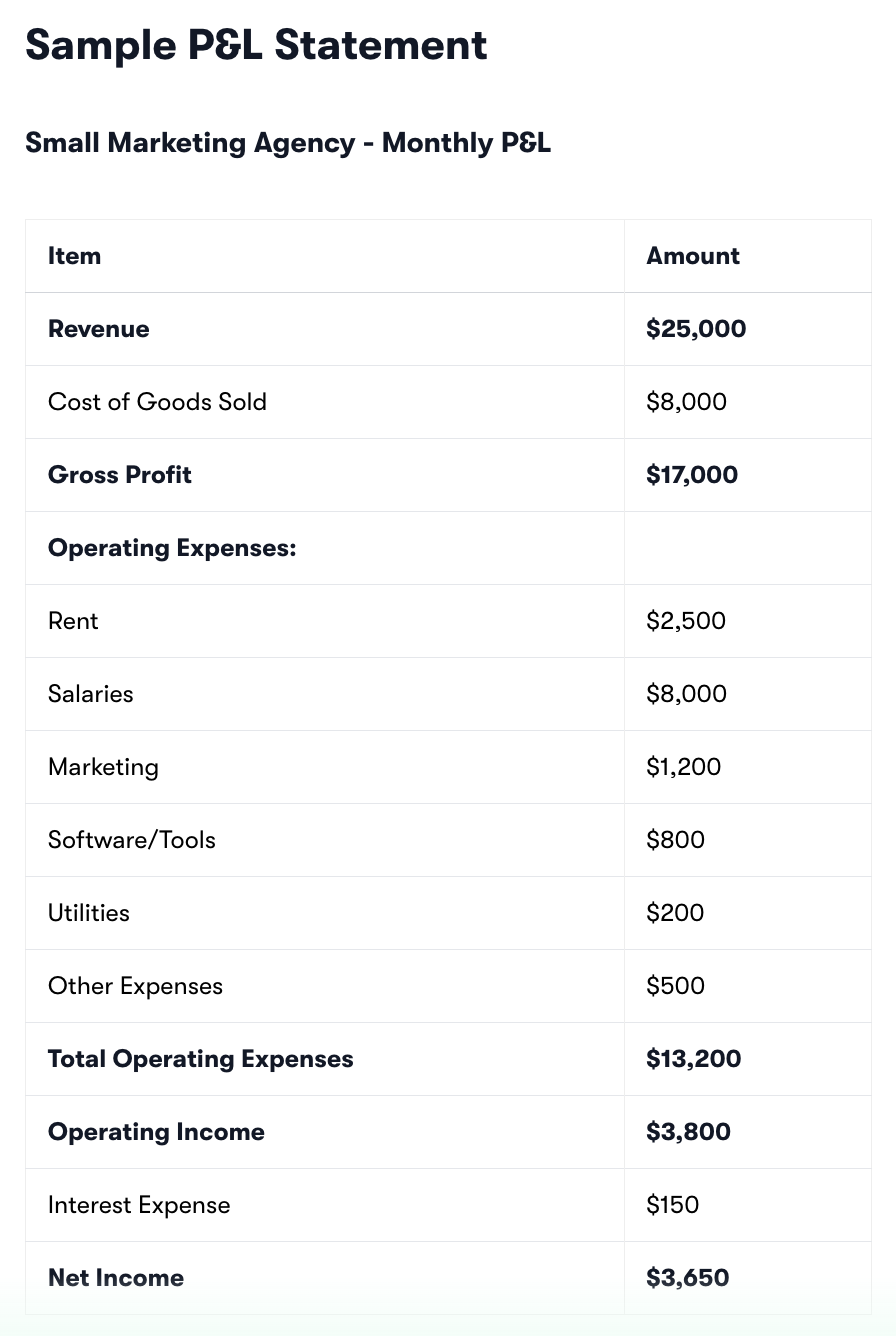
What is a Profit and Loss Statement? Your Business Financial Report Card
A Profit and Loss Statement (P&L) is one of the most important financial documents for any business owner. It's your financial report card that shows whether your business is making money, losing money, or breaking even. Understanding your P&L is crucial for making informed business decisions.
What is a Profit and Loss Statement?
A Profit and Loss Statement, also called an Income Statement, summarizes your business's revenues, costs, and expenses over a specific period (monthly, quarterly, or annually). It shows your bottom line – literally and figuratively.
Simple Purpose: To answer the question "Did we make money or lose money during this period?"
Key Components of a P&L Statement
1. Revenue (Top Line)
Total sales from products or services
Also called gross sales or turnover
The starting point of your P&L
Direct costs of producing your products or services
Materials, direct labor, manufacturing costs
Variable costs that change with sales volume
3. Gross Profit
Revenue minus COGS
Shows profitability before operating expenses
Formula: Gross Profit = Revenue - COGS
4. Operating Expenses
Costs of running your business day-to-day
Rent, salaries, marketing, utilities, insurance
Both fixed and variable operating costs
5. Operating Income (EBITDA)
Gross profit minus operating expenses
Shows profit from core business operations
Formula: Operating Income = Gross Profit - Operating Expenses
6. Other Income and Expenses
Interest income or expenses
One-time gains or losses
Non-operating financial items
7. Net Income (Bottom Line)
Final profit or loss after all expenses
What you actually made or lost
Formula: Net Income = Operating Income - Other Expenses + Other Income
P&L vs. Other Financial Statements
P&L Statement:
Shows profitability over time
Focuses on revenue and expenses
Measures performance
Balance Sheet:
Shows financial position at a point in time
Lists assets, liabilities, and equity
Measures financial health
Cash Flow Statement:
Shows actual cash movement
Tracks cash in and cash out
Measures liquidity
Why P&L Statements Matter
1. Track Business Performance
See if you're profitable month over month
Identify trends and patterns
Measure growth or decline
2. Make Informed Decisions
Where to cut costs
When to invest in growth
Which products/services are most profitable
3. Secure Funding
Banks and investors require P&L statements
Shows business viability
Demonstrates financial management
4. Tax Preparation
Essential for business tax filing
Tracks deductible expenses
Calculates taxable income
5. Set Realistic Goals
Base future projections on historical data
Set achievable revenue targets
Plan expense budgets
How to Analyze Your P&L
Key Ratios to Calculate:
Gross Profit Margin: (Gross Profit ÷ Revenue) × 100
Shows efficiency of core operations
Operating Margin: (Operating Income ÷ Revenue) × 100
Indicates operational efficiency
Net Profit Margin: (Net Income ÷ Revenue) × 100
Shows overall profitability
Red Flags to Watch:
Declining gross margins
Rising expenses faster than revenue
Negative net income for multiple periods
Irregular expense spikes
Common P&L Mistakes
Not preparing statements regularly
Mixing personal and business expenses
Ignoring small expenses that add up
Not categorizing expenses properly
Focusing only on revenue, not profit
Not comparing to previous periods
How to Improve Your P&L
Increase Revenue:
Raise prices strategically
Add new revenue streams
Improve marketing effectiveness
Increase customer retention
Reduce COGS:
Negotiate better supplier terms
Improve operational efficiency
Reduce waste and spoilage
Control Operating Expenses:
Review all recurring expenses
Eliminate unnecessary costs
Negotiate better rates for services
Automate processes to reduce labor costs
P&L Best Practices
Prepare monthly P&L statements
Compare to previous periods
Benchmark against industry standards
Use accounting software for accuracy
Review with your accountant regularly
Focus on trends, not just single months
The Bottom Line
Your Profit and Loss Statement is your business's financial scorecard. It tells you whether your business model is working and where you need to focus your attention. Regular P&L analysis helps you make data-driven decisions that improve profitability.
Make good with your time by reviewing your P&L monthly. This simple practice will give you the financial insights needed to grow your business successfully and avoid costly mistakes.
Remember: Revenue is vanity, profit is sanity. Your P&L keeps you focused on what really matters – making money.